half life formula pharmacology
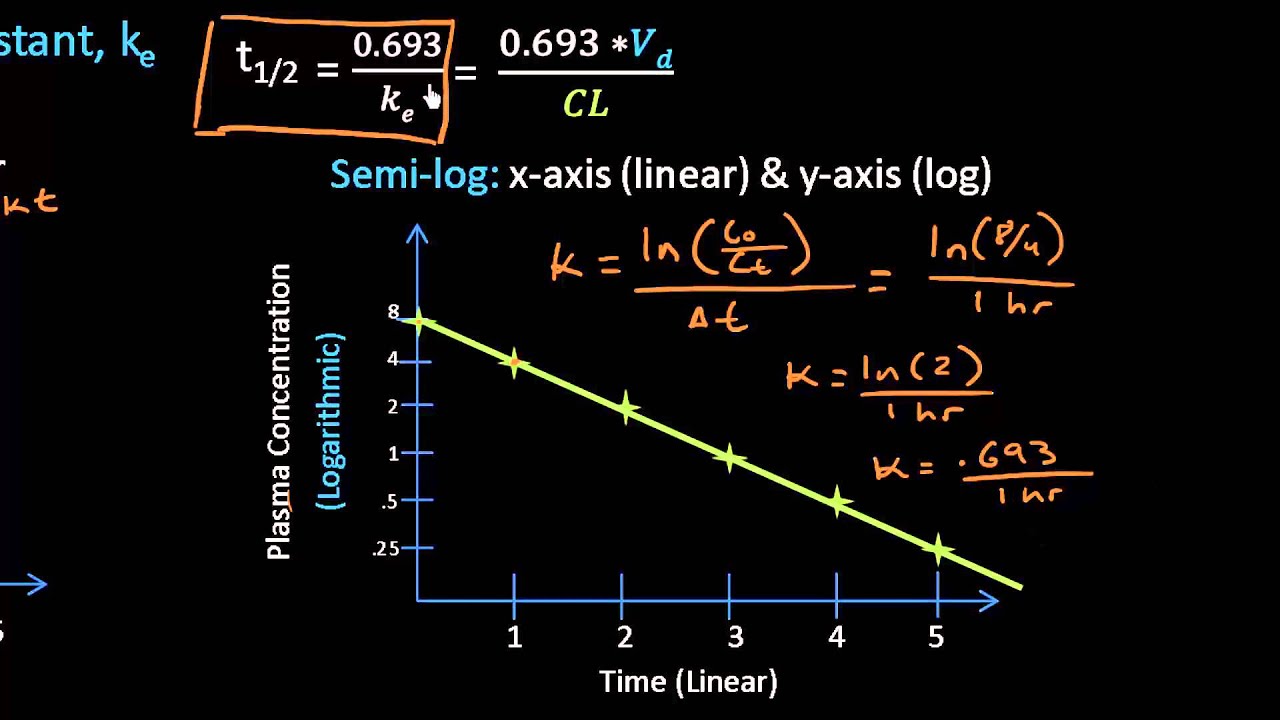
T 1 2 ln 2 V D C L displaystyle t_frac 12frac ln 2cdot V_DCL. Related to the corresponding half-life for the absorption process.
Half Life Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It
Half-life allows the calculation of the time required for plasma concentrations to reach steady-state after starting or changing a dosing regimen.
. T - the half life of a drug. The half-life is directly proportional to the volume of drug distribution. This can be measured by testing for the.
The half-life of a pharmaceutical refers to the amount of time it takes for the concentration of that substance in the body to be reduced by one half. So if you take Ambien after 2 hours the plasma concentration will be reduced to half after 2 more hours the remaining blood levels will be reduced by another half - so a quarter will be left. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology.
In such conditions the observed half-life is called apparent half-life. Plasma half life 12 hours signifies 12 hour is taken for that specific drug to fall its plasma concentration by 50 Absorption is slow Plasma protein binding is high Metabolism is slow Excretion is less Slow sustained action Suitable in chronic case Compliance of the patient is good Frequency of administration is twice a day. Next assume that we stop the infusion.
Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology. This was derived by assuming a 1-compartment model and linear elimination. Half- life t 12 1.
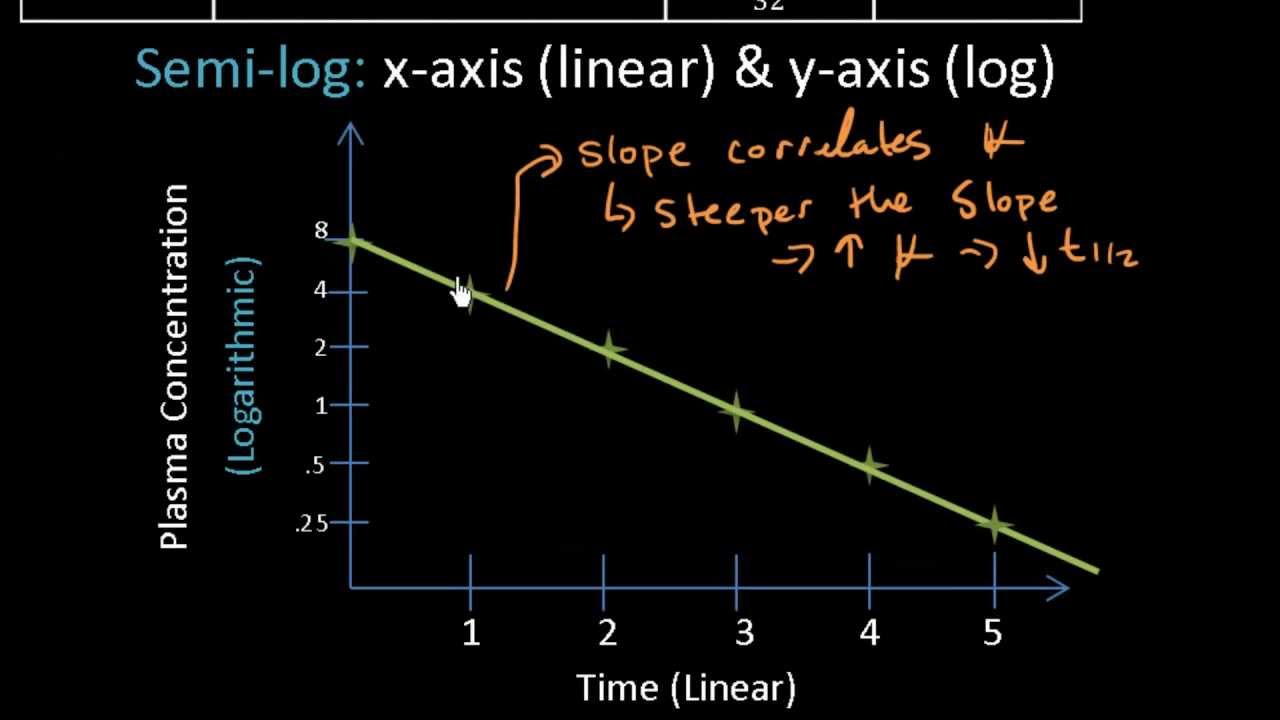
Half-life can be determined mathematically from the elimination rate constant k as. The half-life can be computed simply by dividing the slope of the curve into 0301 the difference between the logarithm of a number C and the logarithm of number half as large C2. Half-life is a first-order kinetic process because the same proportion 50 of the drug is removed during equal periods.
Half-life is used to estimate how long it takes for a drug to be removed from your body. When t t ½ C C o 2 and the equation 87 becomes. It means the more the drug is distributed in the body the more the half-life is.
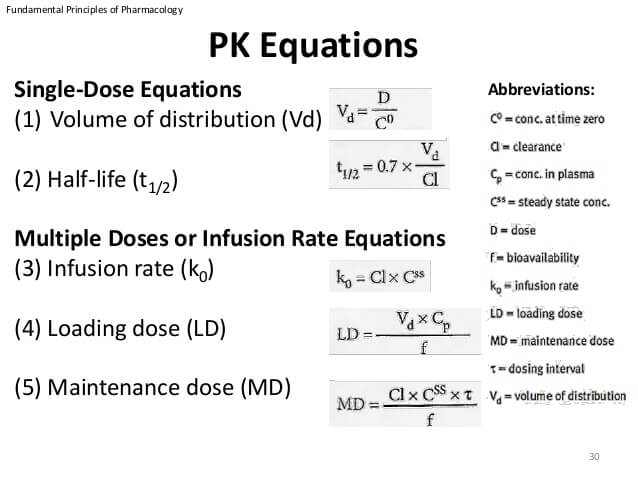
The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable. T12 0693 Volume of DistributionClearance As demonstrated by the formula a drugs half-life is directly dependent on its volume of distribution or how widely the drug spreads throughout the body. Half-life t ½ or half-time is defined as the time period required for the concentration of drug to decrease by one-half.
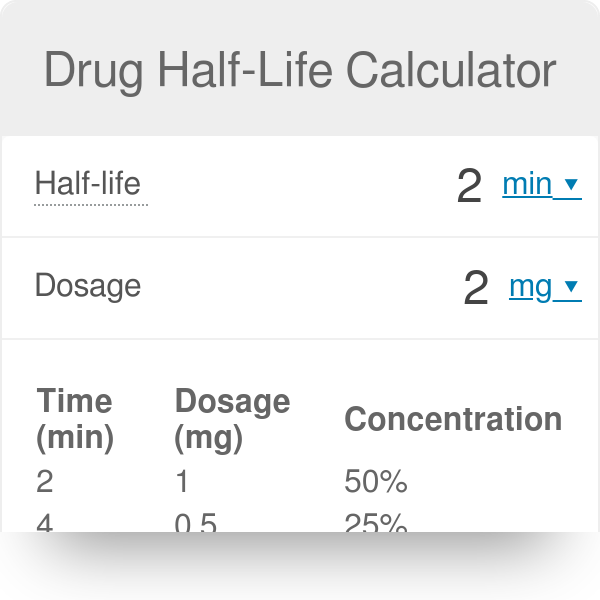
Half-Life The drug half-life t12 is the time required for a drug concentration to decrease by 50. Half-life t12 is the time required to change the amount of drug in the body by one-half during elimination or during a constant infusion. After 2 half-lives 75 of the drug is gone.
T12 0693Volume of distributionClearance or. T - time that has passed since the first original administration of the drug. Heres the formula for half-life.
The half-life of a drug in plasma or serum is frequently taken as indicating the persistence of the drug in its volume of distribution. This interpretation may be. N0 is the initial quantity of the substance that will decay this quantity may be measured in grams moles number of atoms etc Nt is the quantity that still remains and has not yet decayed after a time t.
Intravenous bolus Initial concentration C D 0 Vd Plasma concentration single dose CCe kte 0 ae Plasma concentration multiple dose C Ce e kt k e e 0 1 Peak multiple dose C C e ke max 0 1 Trough multiple dose C Ce e k min ke 0. An exponential decay can be described by any of the following four equivalent formulas. For drugs with first order kinetics this is a constant.
Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug by half. In other words the more widely the drug distributes in your body the longer it half-life. Definition Uses.
The half-life of Ambien is about 2 hours. Equation 2 Equation 2 predicts the time course of drug concentration in the blood from a first-order input process. The symbol for half-life is t12.
Half-life t Vd CL k kee 12 0693 2 0693 ln. After 1 half-life 50 of the drug is gone. Equation 89 shows that the t ½ of a zero-order process is not constant but proportional to the initial concentration of drug C o and inversely.
Authors H Boxenbaum 1 M Battle. The half time or life of a dose represents the period of time in either hours minutes or seconds that it takes a dosage to reach half of its concentration in the plasma after administration. The absorption half- life can be calculated from KA using the natural log of 2 ie absorption half-life 07KA.
By definition t 12 is the time required for the concentration to fall by one half. After 4 5 half-lives we are essentially at steady state concentration. In pharmacology half-life refers to the time it takes for the active substance in a drug to reduce by half.
To do this we are looking for a time t 12 in which This final equation shows the relationship between t 12 and the elimination rate constant. It is basically the peak minus trough concentration divided by the interval. Dosaget Dosage0 05 tT Where.
The formula for half-life is. Assessment t1 2 ln2 λ ln2 V d C L 0693 V d C L t 1 2 l n 2 λ l n 2 V d C L 0693 V d C L Vd volume of distribution CL clearance λ elimination rate constant CLVd. Our drug elimination half life calculator uses the following equation.
Half-life is determined by clearance CL and volume of distribution V D and the relationship is described by the following equation. The time of the peak. In physics half-life refers to the time it takes for a radioactive molecule to disintegrate by half.
Demarcate this time point. The half-life of a drug can vary from a few hours to sometimes weeks depending on how the body processes the drug. The definition of half-life t 12 is the time required for the concentration to fall to 50 of its current value.
Dosaget - the amount. Affiliation 1 Wyeth. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology J Clin Pharmacol.

Drug Half Life Explained Calculator Variables Examples
Loading Dose Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Pharmacokinetic Pk Parameters In Drug Development
First Order Elimination Rate Constant And Half Life A Closer Look Lect 11 Youtube

Elimination Half Life An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Half Life Drug Calculations Practice Problems Part 6 Youtube

Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Pharmacokinetics Mnemonics Epomedicine

Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Back To Basics Pharmacokinetics The Pharmaceutical Journal